Tactical and Operational Levels
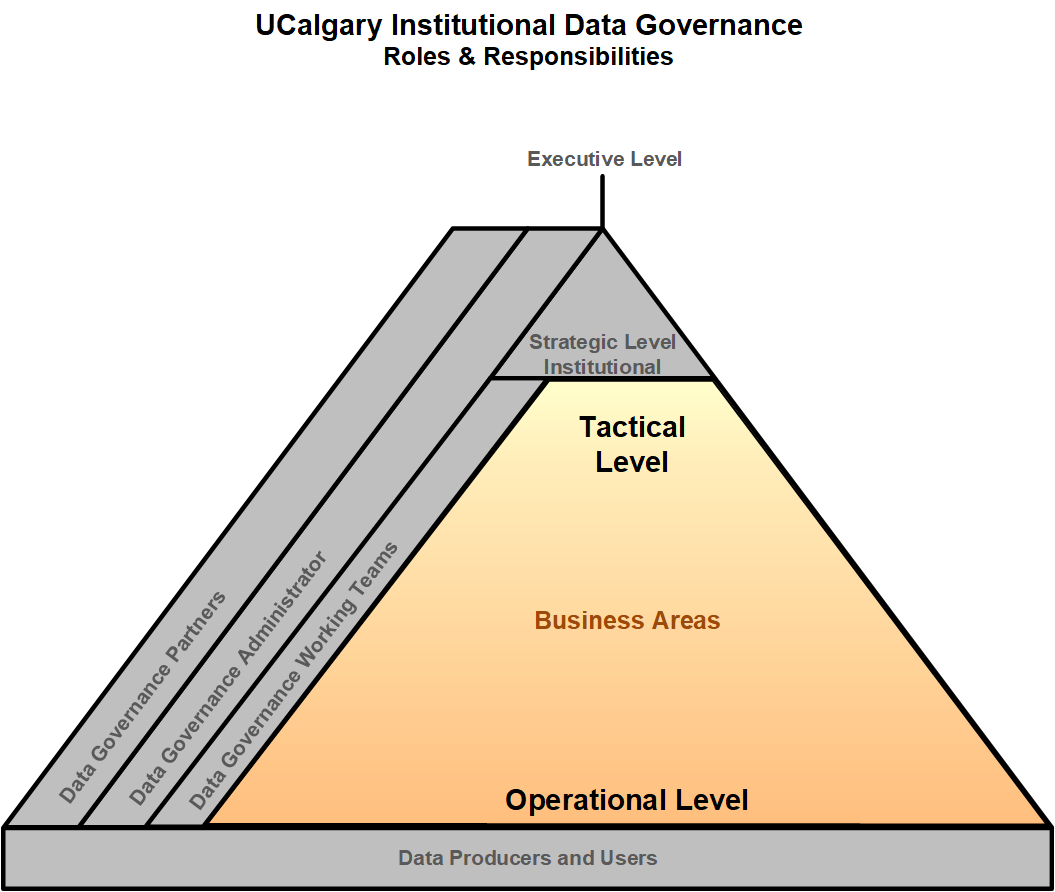
Information Stewards
Information Stewards provide university-level knowledge and understanding for one or more data areas/domains (e.g., student data, financial data, HR data) and oversee life cycle of the data within their business unit. They make data available to the institution, thereby playing a key role at the heart of collaboration, supporting institutional research, assessment, and analytics efforts. This role is critical to the success of business intelligence and analytics programs. Information Stewards work at the tactical and operational levels within their business unit.
Data governance responsibilities (within the business unit):
Information Stewards may designate others (subject matter experts) to assist in carrying out their data governance responsibilities. Information Stewards and their designates collectively have the following responsibilities within their business unit.
Critical Data Elements
- Identify critical data elements for the data subject area.
- Ensure that each data element has a clear definition and is still being used - or retire those that are not - and that adequate documentation is developed, maintained, and communicated appropriately across the business unit.
- Review and approve data definitions, compliance and data classifications (i.e. UCLASS).
Data Quality
- Establish data-quality metrics and requirements, such as defining acceptable values, ranges, and parameters.
- Establish processes and procedures for detection and correction of data issues, contributing expertise to understand the root cause and implement corrective measures.
- Establish procedures and internal controls affecting the quality of data.
- Provide subject matter expertise to guide the discovery, design and development of data solutions focused on achieving quality data in their specific business units.
- Review quality metrics and assessment of progress toward improvements in data quality.
- Prioritize and/or resolve stewardship issues for data elements within the business unit.
- Participate as necessary on Data Governance Working Teams to achieve quality data.
Data Lifecycle
Compile retention, archival, and disposal requirements and ensure compliance with institutional policy, regulations, and business requirements.
Data Access, Privacy, Security, Risk Management
- Oversee access, privacy, security, and risk management pertaining to data in the business unit.
- Define standards and procedures for access to data, including the criteria for authorization.
- Oversight of the access request, approval, provisioning/deprovisioning processes to ensure they are appropriate and commensurate with risk.
- Establish guidelines and protocols that govern the proliferation of data to ensure that privacy controls are enforced in downstream systems and processes.
- Establish information security requirements, including data classification and identification.
- Be informed of regulatory and compliance requirements relevant to the business unit data in order to evaluate risks to its confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
- Establish incident-detection controls.
- Evaluate any suspected or actual breaches or vulnerabilities in confidentiality, integrity, or availability and notify the Data Governance Administrator.
Advocacy and Collaboration
- Advocate for continuous improvement in the use of data as a result of practicing data governance.
- Participate in the collection and development of data documentation and other education / communication materials associated with data in the business unit.
- Ensure data decisions are communicated to the business unit.
- Understand who and how their data is consumed, in and outside the business unit.
- Work to ensure data consumers have an understanding of the data (in order to use effectively).
