Honing my skills, building connections and developing self-confidence through these opportunities has helped me find my “why.” I am a helper, a people person, a student, a learner, a peer and an educator.
Helen Pethrick
BHSc'19, BA'19, MA'21

Experiential learning meets a growing need
Experiential-learning (EL) opportunities support students in discovering their sense of purpose, improving their civic consciousness and employability, and preparing them for leadership roles in their communities and organizations.
In recent years, governments have explored the potential of EL to reduce the shortage of skilled graduates and disruption in the workforce due to automation in our knowledge-driven technology economy.
Types of experiential learning
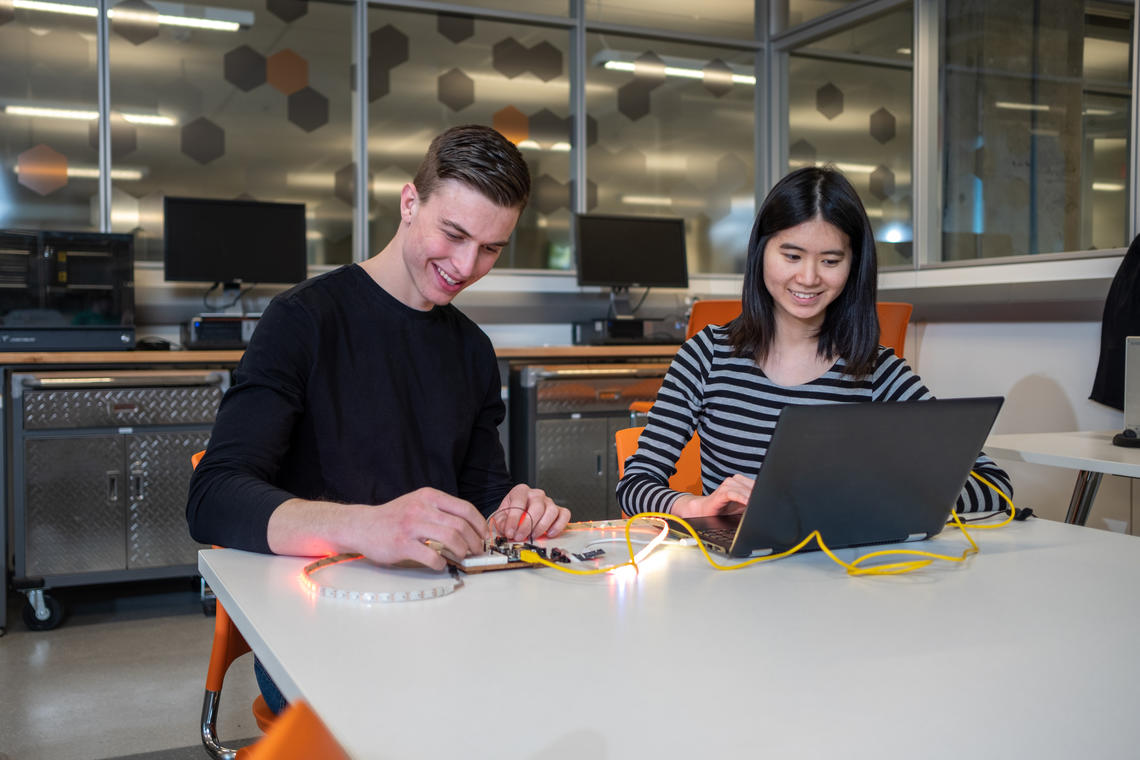
EL often — but not always — takes learners outside of the classroom. It includes internships, field studies, co-ops, laboratories, creative performances, simulations, capstone projects, practicums, undergraduate research and many others.
Students find these types of learning experiences to be deeply engaging and relevant to their future career paths and personal interests. They solve problems and work on projects that resonate with them and they are then able to carry their learning forward and reapply it in different settings.

What are the benefits?
Why should post-secondary institutions be doing more experiential learning?
Our complex and changing world requires graduates to have advanced skills in research, entrepreneurial thinking, collaboration and communication. Through engaging in more EL, post-secondary institutions and governments are addressing the shortage of skilled graduates and disruption in the workforce due to automation in a rapidly evolving economy.
At the University of Calgary, it is critical that our programs integrate hands-on experience with academic study, so that our students are well-equipped as future leaders in industry, government and non-profit.
We need to support the development of more future-ready, highly skilled graduates who will leave university as active citizens ready to drive positive change in the organizations and communities they belong to and serve.

